前言
竞赛中,好的代码风格能提升 debug 效率,以降低被队友揍、队伍内讧和最终打铁的几率。养成好的代码习惯,未来做很多事情都会受益。包括不限于大二大三大四的课程设计,未来参与工作的业绩,婚后的幸福生活……
工欲善其事,必先利其器
纸和笔
整理思路、验证算法,用纸和笔通常会更有效率。
现场赛,代码是经常需要打印出来用纸笔调试的。这个技能十分重要。时间片不可能都拿来给一个题 debug,除非队友别的题没有什么思路。
IDE 准备
| Good ? | So-so ? | Bad ? |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Studio Code
Clion |
Code::Blocks
Visual Studio Dev-C++ |
Vim, GVim
notepad |
在正式 CPC 比赛中,一般只提供 Sublime, VSCode, Code::Blocks, Greany(记不清了), Clion(ICPC only)。
比赛的时候一般都是没有自动代码格式化工具的,需要自己养成良好的缩进习惯。
在2019 CCPC Final中,Visual Studio Code 是装了插件的,应该是 C/C++ 和 Compile and run。别的站我记得都没装。
日常使用,建议用 Visual Studio Code, 装好上面两个插件,然后配置一下缩进规则:
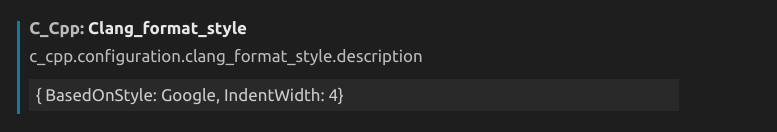
具体表现为:大括号不换号,四个空格缩进。强烈推荐 clang-format。
常用快捷键
- DevC++: Ctrl + Shift + A(AStyle, 低版本没有)
- VSCode: Ctrl + Shift + I(clang-format)
- Clion: Ctrl + Alt + L(记不清了)
缩进
- 4 空格缩进
- 大括号不换行
- for(if, while..) 后面加一个空格
- 双目运算符(+, -, *, /) 等,两边都加上空格
- 大括号不换行,前面加一个空格
- 逗号,同行内的分号后面加一个空格
为未来的代码和 Debug 做好准备
确定数据范围
| Good ? | Bad ? |
|---|---|
const int N = 1100; typedef int td[N][N]; int e[N], d[N]; td f, g, h; |
int u[1100], v[1100]; int q[1100][1100], r[1100][1100], s[1100][1100]; |
明确变量名含义
这里是我常用的命名习惯。代码中的注释只是为了注明含义,正常写代码的时候请不要写这种注释。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110; // upper case N indicates the maximum size of array
const int M = 220; // whatever constant value
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7; // modulus of the answer
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; // +inf, will not overflow when adding
const int INF = 0x7fffffff; // +inf, of i32
struct Node {
int v;
int to;
int next;
bool operator<(const Node& n) const {}
};
// !!! bad
int next, prev, x1, x2, y1, y2; // you should never use these names
// becase they are already defined
int a[N]; // original value
int d[N]; // data or dp array
int cnt, ans; // count, answer
vector<int> primelist; // if it has compilcated meaning, use full name instead
// prime_list is a bit awkward, imo
bool vis[N]; // visit mark
vector<int> v; // vector
priority_queue<int> q; // queue
/** whichever is just fine */
typedef long long LL;
typedef long long ll;
/* some frequently used functions */
template <class T>
T read(); // optimized read
template <class T>
void read(T& t); // anoter version of optimized read
int gcd(int a, int b);
int fp(int a, int n, int m /* modulus */); // fast pow
void exec() /* solve a single test case*/ {
int n; // scope
cin >> n;
for (int i /* iterator(index) */ = 0, t /* temp value */; i < n; i++) {
cin >> t;
a[i] = t;
v.push_back(t);
}
for (auto it /* vector<int>::iterator */ = v.begin(); it != v.end(); ++it) {
// do something
}
for (const auto& e /* element */ : v) {
// do something
}
}
int main() {
int T; // upper case, T test cases
cin >> T;
while (T--) exec();
}
逻辑段换行
在上面的代码中也有体现。
逻辑相差很大的代码块间应加入换行,如 初始化 / 输入 / 计算 / 输出 。
除非是封装的很好的模板,不要压行
不然你早晚有重新把他展开 debug 的时候,炸心态 + 1。
把大括号打上
| Good ? | Bad ? |
|---|---|
if (true) {
do_something();
}
|
if (true) do_something(); |
因为你很难一次把代码写完整,更何况有时候还需要在分支 debug,建议一直把大括号加上。这会节约不少时间,并能有效缓解 debug 时的烦躁。
把头文件加上
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
永久解决头文件没加的问题。
不过这个也有 side-effect
- 如果不清楚编译环境如何,可能会爆 0(如蓝桥杯、OI等)。除非你有非常确定的信息来源表明可以用这个头文件,不然不要用。
- 不太好用的 IDE(说的就是Dev-C++),代码补全可能会出现问题。
用注释代替删除
不要自信满满删除“错误代码”和 debug 代码(比如一些 cout 或者 printf)。
你可能在后面察觉到问题,然后在敲一遍。(这很炸心态)
赛场不是炫技的地方
不要用除你之外谁都看不懂的高级语法
除非你能绝对 carry,否则你要考虑你的队友能不能看懂你的代码。
而且,比赛的时候大多是 C++11 或 C++14,C++17 通常并不支持。
不要在比赛的时候搞复杂的面向对象
写继承多态 biss。
但是 struct 里写成员函数,重载运算符什么的还是要会的。
class T {
int a;
bool operator<(const T& b) const { return a < b.a; }
};
不要在比赛的时候写非固定搭配的位运算
编译器比你想象的聪明得多,而且你的代码差的并不是你想象中 n << 1 比 n * 2 快的那部分时间(更何况根本没快)。
别给自己找麻烦。
#include <iostream>
int c(int a, int b) { return a << 1 + 1; }
/**
_c(int, int):
lea ecx, [rsi+1]
mov eax, edi
sal eax, cl
ret
*/
int _c(int a, int b) { return (a << 1) + 1; } // what's wrong with you??
/*
c(int, int):
lea eax, [rsi+rdi*2]
ret
*/
int d(int a, int b) { return a * 2 + 1; }
/**
d(int, int):
lea eax, [rsi+rdi*2]
ret
*/
int main() {}
9102 年了,不要用 register 关键字了!!
不要是个函数就加 inline ,T 了改成 inline 该 T 还 T。
除非是形如 x & -x 这种固定搭配,不然不建议使用位运算。
如果非要使用的话,请打上括号。
不要你觉得,要评测机觉得
赛前热身赛要试的东西
-
- 是否忽略行末空格
- 是否有 Presentation Error (有时候 Presentation Error 会直接判 Wrong Answer )
- 评测机是否有 __int128 (解决爆 long long 的 plan B)
- VS Code 是否有插件
- 编译器设置 (比赛用的 Code::Blocks 有时候会闪退)
- Python 环境
- 插排,电源键在哪(看好别碰!)
厕所在哪
不要在没绝对把握的情况下飞裸指针和动态内存分配
| Good ? | Bad ? |
|---|---|
const int N = 1100; int d[N]; |
int n = 1100; int d[n]; int n = 1100; int *d = new int[n]; delete[] d; |
不确定就换 long long
除非你非常非常确定炸不了 int ,请尽可能使用 long long 。
不确定就把 memset 写上
当输入数据会覆盖整个数组,或生成数组时不依赖后面的数据(即不存在 d[x] = f(d[x+n]), n >= 0 )时, 的确不需要 memset。
但是如果你不清楚的时候,最好在每组测试数据之前 memset。
常用的 memset 操作
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;
int d[3];
inline void print() {
copy(d, d + 3, ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
// actually redundant,
// because array defined outside always has initial value 0
memset(d, 0, sizeof(d)), print();
// 0 0 0
// +inf
memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof(d)), print();
// 1061109567 1061109567 1061109567
// -inf
memset(d, 0xbf, sizeof(d)), print();
// -1077952577 -1077952577 -1077952577
// -1
memset(d, -1, sizeof(d)), print();
// -1 -1 -1
}
能抓到耗子的猫就是好猫
尽量避免刻板教条的 old-school code
| Good ? | Bad ? |
|---|---|
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
int f() {
// implementation
}
int g() {
// implementation
}
int main() {}
|
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
int f();
int g();
int main() {}
int f() {
// implementation
}
int g() {
// implementation
}
|
数组开大点
| Good ? | Bad ? |
|---|---|
// suppose you need an array to contain n numbers, // where n is given in input file and n < 1000 // good int e[1100]; |
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
// suppose you need an array to contain n numbers,
// where n is given in input file and n < 1000
// may cause underlying error
int e[1000];
// are you cxk?
int f[110000];
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
// you are even worse than cxk
int *d = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
free(d);
}
|
不“清真”的代码不要紧,能解题就行
混合 C 语言的一部分内容
scanf, printf, getchar 远远快过 cin 和 cout。
除非输入量特别小,请一直使用 scanf / printf。
cin / cout 不过的 scanf / printf 可能过。scanf / printf 不过的 getchar / putchar 基本*一定不过。
*不包括校内 OJ 部分老题
Array starting from 1 is not devil
数组从 0 开始有时候会带来很多问题,比如:
- 处理边界,防止越界很困难
- 题目从 1 开始的时候还要费劲想
- 前缀和不方便
但不是让你什么时候都从 1 开始,大部分时候从 0 开始更方便。这个需要具体情况具体分析。
变量能全局就全局
在函数外定义的数组等都是直接在静态区上分配的内存,而且都有初值 0。
尤其是特别大的数组,不要在函数内部开(在栈上分配,需要 memset,还容易炸)。
更何况给每个函数传引用或者指针真的很烦。
快速换 long long
#define int long long ,然后去掉 main 的返回值。
如果使用了 scanf / printf 记得将 %d 改为 %lld!
如果使用了 clang 做编译器,会直接 CE。
#include <iostream>
#include <limits>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
main() {
int n = numeric_limits<int>::max();
cout << n << endl;
// 9223372036854775807
}
一些可以节省时间的写法
使用 auto (C++11)
C++11C++ 已经实现了比较智能的类型推导。可以使用 auto 实现非常复杂的类型定义。
更高级的使用方法(decltype等)请自行研究。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<pair<int, int>> v;
int main() {
vector<pair<int, int>>::iterator it;
auto b = v.begin();
return 0;
}
遍历 C++ 容器(以 std::map 为例)
C++11 C++17// C++11
for (map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); ++it) {
cout << it->first << ' ' << it->second << endl;
}
// C++11
for (auto it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); ++it) {
cout << it->first << ' ' << it->second << endl;
}
// C++11
for (const auto &e : m) {
cout << e.first << ' ' << e.second << endl;
}
// C++17
for (const auto &[key, value] : m) {
cout << key << ' ' << value << endl;
}
![]() 本作品使用基于以下许可授权:Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
本作品使用基于以下许可授权:Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.